What is the Breath Holding Duration of a Dolphin? Dive to Discover the Secrets of This Marine Wonder

how long can a dolphin hold its breath
Introduction
Every now and then, people are left wonderstruck by the dolphins because they are often seen swimming and diving deep into the ocean. Have you wondered about the breath holding span of a dolphin? Although dolphins might seem to be fish, they are as much a mammal as humans. This implies that they need to surface for air. During extensive submersible swimming, how do they manage prolonged periods without respiration? This article outlines the incredible strategies utilized by dolphins to adapt and cope in their natural aquatic environments. We shall look at their anatomy, how dolphins sleep without drowning, and all the pertinent details we shall explore deep.
How Do Dolphins Exhale and Breathe and their Special Features?
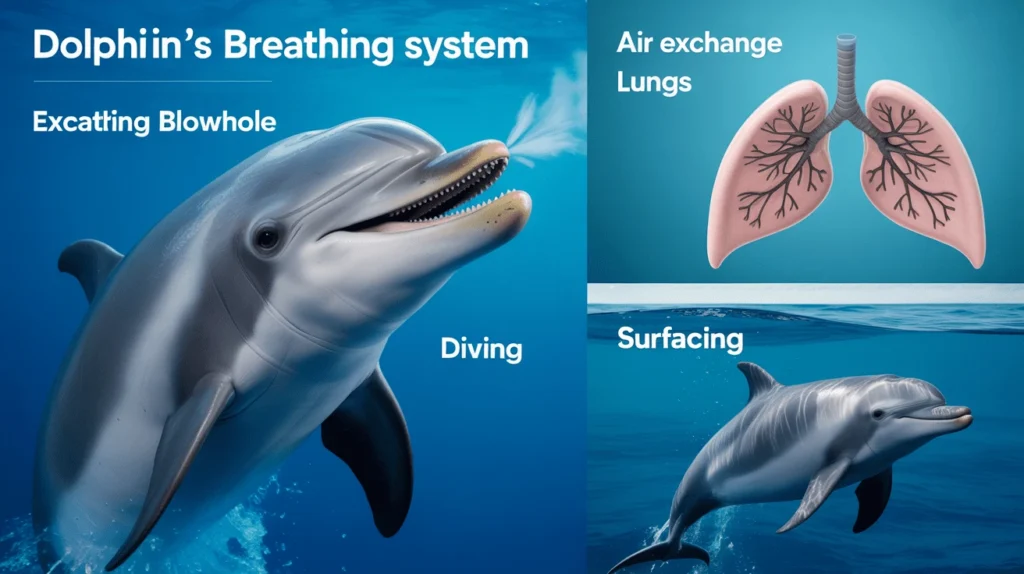
Unlike fish that utilizes gills, a dolphin uses lungs to breathe. They are warm-blooded mammals capable of viviparous reproduction. Like humans, they also require oxygen. What separates them from us is the timing of breathing and the method employed.
Dolphins possess a unique breathing organ termed a blowhole situated on the top of their heads. This anatomical feature allows them to take rapid gas exchanges while their body remains submerged in water. With the assistance of powerful lungs and muscular control, a dolphin can exhale and inhale in under a second.
This allows dolphins to exhale and inhale in under a second. Like all marine mammals, their respiratory system is adapted for efficiency. As with all marine mammals, dolphins do not breathe continuously. Instead, they take one significant breath and subsequently dive. Additionally, dolphins are capable of exchanging as much as 80 to 90 percent of air within their lungs in a single breath, a feat far superior to humans who can only exchange around 15 percent of air within their lungs.
How Long Can Dolphins Hold Their Breath Underwater?
Now to the big question, how long can a dolphin hold its breath? The average dolphin is capable of holding their breath for 8 to 10 minutes, however, certain species are capable of remaining submerged for as long as 15 minutes.
How long these individuals are able to hold their breath will depend on the particular species along with the activity they are engaged. For example, dolphins are able to hold their breath longer while swimming slowly or resting. Conversely, they are more likely to surface frequently during active, hunting, or playful behavior.
Related questions: How long can dolphins remain submerged?
Dolphins tend to emerge for air every 3 to 5 minutes during fast swimming or social behavior. However, rest periods can extend to closer to 10 minutes submerged.
Breathe Evaluation: Can a Dolphin Live or Breathe Out of Water?
Can dolphins breathe outside the water? This question arises frequently. The answer is affirmative, but only temporarily. As air is ingested through their blowhole, they can remain above water hypothetically floating on it while expiring. However, this is not sustainable.
On dry land, their massive, buoyant bodies would make internal organ damage highly probable. Furthermore, their hydrating skin would swiftly dry without water, resulting in serious injury or death. Thus, while air allows them to function, it becomes lethal in excess.
Related question: How long can a dolphin survive without water?
In controlled environments, dolphins have been documented to endure several hours out of water given constant hydration and cooling. However, unsupported, most would not surpass a couple of hours.
Considerations Influencing Breath-Holding Capacity in Dolphins
Different dolphins are not identical. Several elements determine the breath-hold limit in dolphins:
1. Species:
Distinct species of dolphins possess varying skills. For instance, the bottlenose dolphin, which is extensively researched, typically holds its breath for 8 to 12 minutes. Certain deep-diving spinner dolphins may exceed this limit.
2. Activity Level:
Diving and swimming at high speeds require considerable oxygen. As such, dolphins will need to come up for air more frequently. Resting dolphins have a greater ability to extend their breath-holding capacity.
3. Age and Health:
Dolphins that are aged or youthful tend not to hold their breath as efficiently compared to healthy adults. As with people, physical health status is important.
4. Water Conditions:
Cold water, as well as increased depth, can demand more energy, affecting breath intervals.
Bottlenose Dolphin: An Example of Breath-Holding
The bottlenose dolphin is perhaps the best known of the dolphin species. They can be found in aquariums, shows, and research programs. They are famous for their intellect and good swimming skills.
The typical bottlenose dolphin can hold its breath while diving for an average duration of about 10 minutes. During more vigorous activity, they can surface every 2 to 3 minutes, but during rest or slow movement, this duration can increase to 10 to 12 minutes.
Bottlenose dolphins with specially designed lungs have the ability to collapse under deep breath safely. This allows them to dive deeper than most marine animals without risk of injury.
How Do Dolphins Sleep Without Drowning?
Do dolphins sleep? Yes, but differently when compared with humans.
For dolphins, one-sided sleeping is referred to as unihemispheric slow-wave sleep. This is when only one side of the brain can rest, while the other half remains awake to control essential functions such as breathing and monitoring for possible threats.
This enables them to rest without losing all consciousness. They tend to float or swim slowly some inches below the surface, surfacing to breathe automatically every few minutes.
Related question: Where do dolphins sleep?
Dolphins sleep in the open ocean or near coastal areas. These regions are usually quieter and safer where they are not monitored by predators. Like other marine mammals, they do not have nests or caves like terrestrial animals. Their sleep occurs throughout the day and is generally light and very fragmented.
Dolphin vs Whale Breath-Holding Abilities
Cetaceans include both dolphins and whales, as they belong to a single biological group. However, the size discrepancy is quite large between the two, as one family contains relatively smaller species and the other larger.
Sperm whales are one of the whale species, and they can hold their breath for over an hour. Their physiological adaptation to deep diving includes larger reserves of oxygen, as well as a slower heart rate while submerged.
Dolphins as opposed to whales are more social and active. Though they do not come close to the performance of underwater mammals, these creatures do surpass the vast majority of land mammals when it comes to breath-holding stamina.
The related question that stems here is: “How long can whales hold their breath?”
Most whale species reportedly do not exceed 60 minutes of diving, rather spending an average of 20 minutes to 60 minutes underwater depending on the whale’s size and activity.
Q&A Section Q: Are dolphins mammals?
Dolphins are considered as mammals as they breathe air, give birth to live young and nurse their babies with milk, all characteristics of a mammal.
Q: Can dolphins breathe through their mouths?
Breathing through the mouth is solely reserved for terrestrial creatures, hence dolphins cannot breathe through their mouths at all. Amidst the rules of their physiology, dolphins can only breathe via their blowholes.
Q: How deep can dolphins dive?
Depths of 200 to 500 feet are frequented by most dolphins, however some species are capable of greater depths. There are deep-diving dolphins that may exceed 1000 feet.
Q: What is the outcome of a dolphin being unable to reach the surface to breathe?
Fishing nets pose a huge risk to dolphins because they can entrap these animals, preventing them from surfacing to breathe. Fishing net entanglement can lead to drowning in air-breathing species, such as dolphins.
Q: What about dolphins forgetting to breathe?
Voluntarily breathing means dolphins have full control over their respiration and even while dormant, they have the ability to “switch off” their breath.
Summary: The Wonders of Breath
On a dolphin’s average, its breath is 8 to 10 minutes, with some species even able to reach 15 minutes under certain conditions. These remarkable marine mammals have developed specific adaptations that allow them to thrive efficiently breathe underwater and alongside certain species, sleep while remaining vigilant.
Dolphins are optimally tailored for life in the ocean and from their powerful lungs to sophisticated sleeping behaviors, there is always something to learn from nature. For students, marine life enthusiasts, or even curious individuals, these intelligent beings invite inquiry; exploration about dolphin still awaits.
So, when you spot a dolphin surfacing to leap over the waves, remember that the extraordinary magic only begins with what meets the eye.



